Understanding how to find velocity is essential in physics, engineering, and everyday motion analysis. Velocity measures the rate of change of position with direction, distinguishing it from speed, which only accounts for magnitude. Accurate velocity calculation is vital for analyzing moving objects, predicting motion, and solving problems in mechanics, kinematics, and dynamics.
This comprehensive guide explains how to find velocity in physics using multiple methods: from acceleration, position-time graphs, distance and time, to advanced concepts like center of mass velocity. Each method includes step-by-step explanations, examples, and formulas, ensuring clarity for beginners and advanced learners alike.
By mastering velocity calculations, students and professionals can confidently solve kinematics problems, interpret motion graphs, and apply physics to real-world scenarios like car motion, projectile motion, and rotating systems.
How to Find Velocity in Physics

Understanding Velocity in Physics
Velocity in physics is a vector quantity that measures both speed and direction. Unlike scalar speed, velocity provides information about how fast and in which direction an object moves. It is crucial in kinematics, projectile motion, and mechanics for describing motion accurately.
Key Points to Find Velocity in Physics
• Identify the initial and final positions
Determine the object’s displacement, not total distance. Displacement measures how far the object is from the starting point in a straight line.
• Determine the time interval
Accurately measure the duration over which displacement occurs. Time is critical because velocity is proportional to displacement over time.
• Use the basic velocity formula
Velocity = Displacement ÷ Time. Ensure the direction of motion is accounted for, as velocity is a vector.
• Apply vector notation when necessary
Represent velocity with arrows or unit vectors to indicate direction, especially in two or three dimensions.
• Convert units consistently
Keep distance and time in compatible units, such as meters and seconds, to avoid errors in calculation.
• Verify with motion graphs
Cross-check calculations using position-time or displacement-time graphs to ensure consistency.
Understanding these basics establishes a solid foundation for more advanced velocity calculations.
Also Read:- How to Find Archived Emails in Gmail: Complete Guide
How to Find Velocity from Acceleration

Velocity from Acceleration Explained
Velocity can be derived from acceleration, which measures the rate of change of velocity over time. If acceleration is constant, the final velocity is calculated using kinematic equations. This is widely used in mechanics for objects under uniform or varying acceleration.
Step-by-Step Approach
• Identify initial velocity (u)
The velocity at the starting point is crucial. It may be zero if the object starts from rest or a known value from measurements.
• Determine acceleration (a)
Measure or obtain the acceleration, ensuring consistent units like meters per second squared (m/s²).
• Measure the time interval (t)
Acceleration must be applied over a known duration to find the change in velocity accurately.
• Apply the kinematic equation
Final velocity (v) = u + a × t. This formula assumes constant acceleration over time.
• Consider direction
Acceleration and velocity are vector quantities. Pay attention to the direction to interpret positive or negative changes.
• Verify with displacement equations
Use s = ut + ½at² for cross-verification in physics problems, ensuring your velocity calculation aligns with observed motion.
Calculating velocity from acceleration helps analyze freely falling objects, vehicles, and any motion under forces.
Also Read:- How to Use a Compass: A Complete Guide for Navigation in the Real World and Beyond
How to Find Velocity from Position-Time Graph
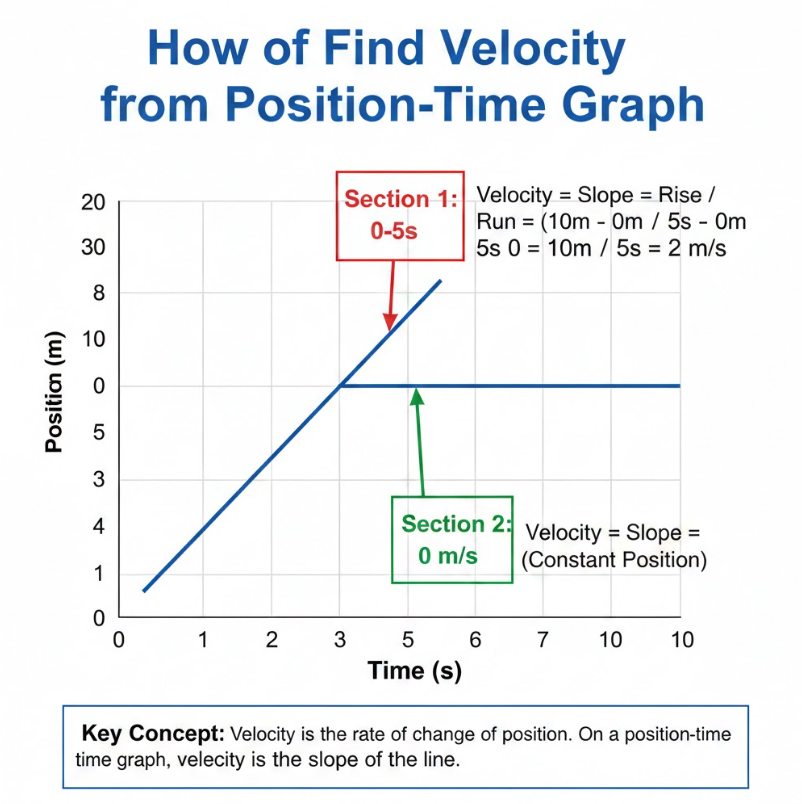
Velocity from Position-Time Graph Explained
A position-time graph shows an object’s displacement over time. The slope of this graph represents the velocity, providing a visual method to calculate velocity without formulas. Positive slopes indicate forward motion; negative slopes indicate motion in the opposite direction.
Step-by-Step Process
• Identify points on the graph
Choose two points on the straight line or curve for calculation. This allows accurate slope determination.
• Determine change in position (Δx)
Measure vertical difference between the two points on the displacement axis. This is the displacement over the chosen interval.
• Determine change in time (Δt)
Measure horizontal difference between the points on the time axis.
• Calculate slope
Velocity = Δx ÷ Δt. This provides the average velocity between two points.
• Consider direction
Positive slope = positive velocity, negative slope = negative velocity.
• Apply for curves
For changing velocity, take the tangent line to the curve at a specific point to find instantaneous velocity.
This method is ideal for experiments where motion is recorded graphically.
Also Read:- How to Check Engine Oil: A Complete Practical Guide for Every Car Owner
How to Find Velocity with Distance and Time

Velocity Using Distance and Time Explained
When displacement and time are known, velocity is calculated as displacement divided by time. This is one of the most fundamental and straightforward methods to find velocity.
Practical Method
• Measure displacement accurately
Use straight-line measurement for vector displacement rather than total path length.
• Record time taken
Use a stopwatch or timer, ensuring accurate measurement to minimize errors.
• Apply velocity formula
Velocity = Displacement ÷ Time. This gives average velocity over the period.
• Account for direction
Indicate whether motion is forward, backward, or along a vector path.
• Check for units
Ensure distance (meters) and time (seconds) are consistent to obtain velocity in m/s.
• Use examples for practice
For instance, if a car travels 100 meters in 10 seconds, velocity = 100 ÷ 10 = 10 m/s.
This method is widely applied in basic physics problems, traffic analysis, and sports motion studies.
Also Read:- How to Make Matcha Latte: A Complete Guide for Cafe-Quality Results at Home
How to Find Velocity Without Time
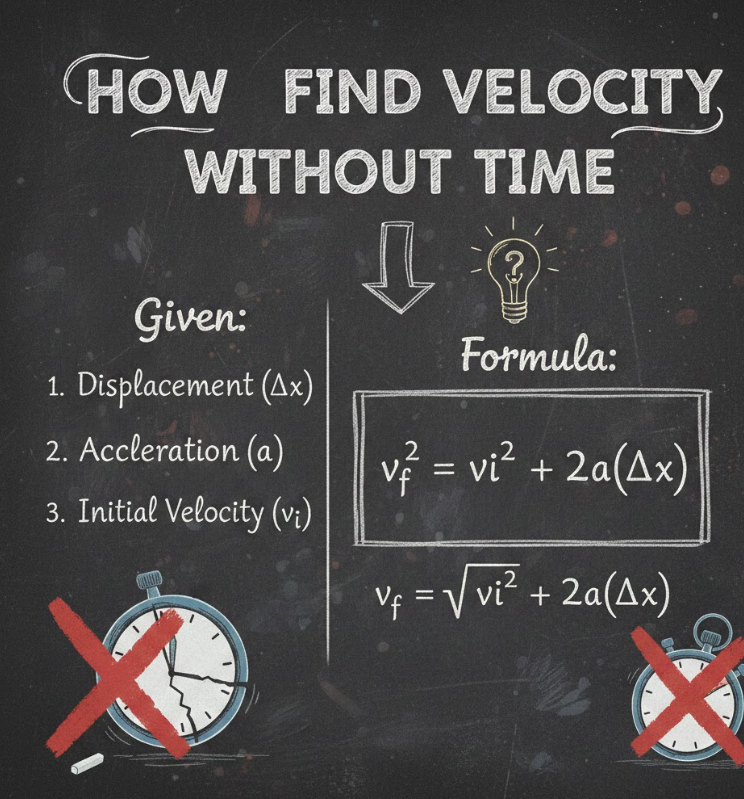
Velocity Without Time Explained
In some scenarios, time is unknown, but acceleration and displacement are available. Using kinematic equations, velocity can still be calculated efficiently. This is common in free-fall and constant acceleration problems.
Steps to Calculate Velocity Without Time
• Determine initial velocity (u)
Record or assume starting velocity based on problem context.
• Determine acceleration (a)
Obtain constant acceleration value.
• Measure displacement (s)
Find the distance covered during acceleration.
• Apply kinematic formula
v² = u² + 2as. Solve for v by taking the square root.
• Consider direction
Velocity is vectorial; ensure sign conventions match motion direction.
• Check consistency
Cross-check by plugging into alternative equations for verification.
This approach is essential when timing devices are unavailable or motion occurs over known distances.
Also Read:- How to Ice Skate: A Complete Beginner-to-Advanced Guide
How to Find Velocity of Center of Mass
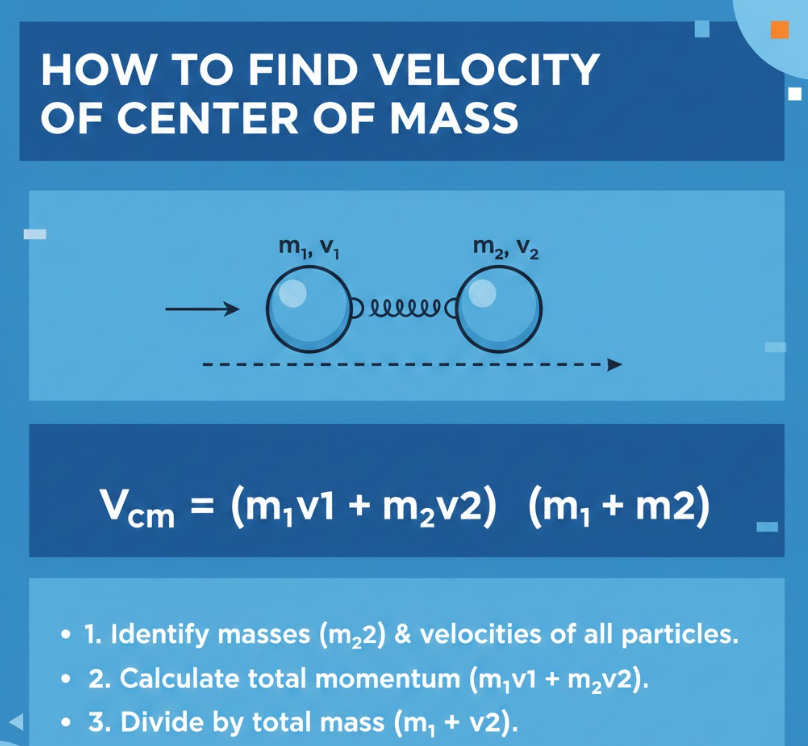
Velocity of Center of Mass Explained
The velocity of the center of mass (COM) represents the average motion of a system’s mass. In multi-particle systems, it helps analyze motion, collisions, and momentum conservation.
Step-by-Step Method
• Identify individual masses (m₁, m₂ …)
Determine all masses in the system accurately.
• Determine velocities of each mass (v₁, v₂ …)
Measure or calculate the velocity of each particle.
• Apply the formula
V_com = (Σ mᵢvᵢ) ÷ Σ mᵢ. This calculates mass-weighted average velocity.
• Consider direction
Each velocity is vectorial; apply vector addition if motion occurs in 2D or 3D.
• Use for momentum calculations
Center of mass velocity is key in elastic and inelastic collisions.
• Cross-check system momentum
Total momentum = total mass × V_com, ensuring the solution is consistent.
Calculating COM velocity is fundamental in physics, engineering, and biomechanics.
Also Read:- How to Mince Garlic – Complete Beginner to Expert Guide
Common Mistakes When Finding Velocity
• Confusing speed with velocity
• Using total distance instead of displacement
• Ignoring direction in vector quantities
• Wrong units for time or displacement
• Forgetting vector addition in multi-dimensional motion
• Skipping verification with graphs or alternative formulas
Avoiding these mistakes ensures accurate velocity calculations.
Conclusion: Mastering How to Find Velocity
Understanding how to find velocity is essential in physics. By using displacement, time, acceleration, graphs, or center of mass methods, you can analyze motion accurately. Velocity calculations are foundational in mechanics, sports science, engineering, and everyday motion studies. Mastery requires practice, attention to vector direction, and careful unit usage.
Whether calculating average or instantaneous velocity, using kinematic equations, or analyzing motion graphs, the techniques in this guide equip students and professionals to solve a wide range of problems efficiently.
FAQs
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Velocity is a vector quantity (magnitude + direction); speed is scalar (magnitude only).
How do I find instantaneous velocity?
Use the slope of the tangent on a position-time graph at the specific point.
Can velocity be negative?
Yes, negative velocity indicates motion in the opposite direction.
What is the fastest method to find velocity in experiments?
Using displacement-time measurements or motion sensors provides rapid and accurate results.
For More Info Visit Hola-Fly